|
|
|
A CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±2 kHz Nominal frequency response = 0.4 kHz Maximum frequency response = 2 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
B CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±4 kHz Nominal frequency response = 0.8 kHz Maximum frequency response = 4 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
C CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±8 kHz Nominal frequency response = 1.6 kHz Maximum frequency response = 8 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
D CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±16 kHz Nominal frequency response = 3.2 kHz Maximum frequency response = 16 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
E CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±32 kHz Nominal frequency response = 6.4 kHz Maximum frequency response = 32 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
F CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±64 kHz Nominal frequency response = 12.8 kHz Maximum frequency response = 64 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
G CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±128 kHz Nominal frequency response = 25.6 kHz Maximum frequency response = 128 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
H CHANNELS Deviation limits = ±256 kHz Nominal frequency response = 51.2 kHz Maximum frequency response = 256 kHz Center Frequency (kHz) |
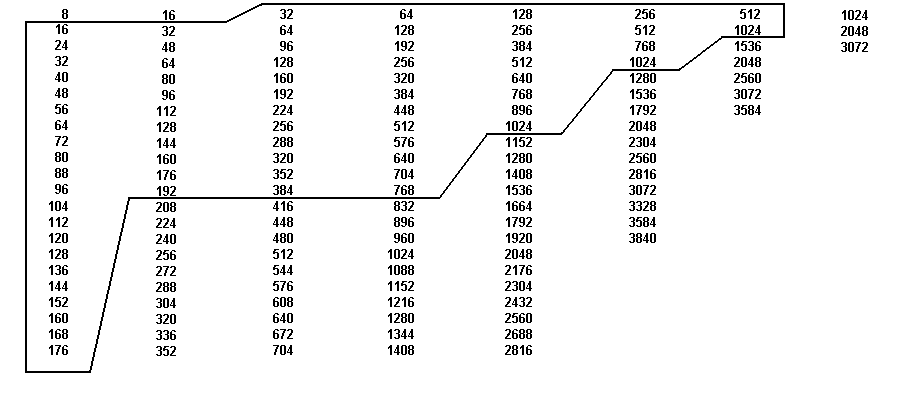  The constant-bandwidth channel designation shall be the channel center
frequency in kilohertz and the channel letter indicating deviation limit;
for exapmle, 16A, indicating fc = 16 kHz, deviation limit of ±2 kHz.
The constant-bandwidth channel designation shall be the channel center
frequency in kilohertz and the channel letter indicating deviation limit;
for exapmle, 16A, indicating fc = 16 kHz, deviation limit of ±2 kHz.The indicated maximum frequency is based upon the maximum theoretical response taht can be obtained in a bandwidth between deviation limits specified for the channel. See discussion in appendix B for determining practical accuracy versus frequency response trade offs. Prior to using a channel outside the enclosed area, the user should verify the availability of range assets to support the demodulation of the channel selected. Very limited sipport is availbale above 2 MHz. |